In This Article
In the context of global economic turbulence, the fashion industry is confronting unprecedented challenges. Escalating raw material costs, increased logistics and transportation expenses, and declining consumer purchasing power are compelling brands to adjust their business models to navigate multiple pressures. Particularly in an environment where rising retail prices lead to reduced consumer spending capacity, balancing profitability with price competitiveness has become a central issue for many fashion brands. This article explores how, amid inflation and rising costs, fashion brands can implement a series of optimization measures to reduce expenses, enhance efficiency, and maintain market competitiveness without sacrificing profits.
Global Economic Context and Cost Pressures in the Fashion Industry
Inflation: Global Economic Uncertainty
In recent years, global economic uncertainty has intensified significantly. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the global inflation rate reached approximately 8.8% in 2023, a substantial increase compared to the average of the past decade. This surge in inflation has been particularly pronounced in major economies such as the United States, Europe, and China. Rising costs of raw materials, energy, and labor have become unavoidable burdens in business operations. In the fashion industry, these escalating costs directly impact the cost structure of production processes.
In 2023, the prices of key production materials like textiles and leather increased by 20% to 30%. This surge was especially notable in the production of natural fibers and leather goods, where price hikes directly influenced the final Retail Prices of products. For many brands, this necessitated a reevaluation of raw material procurement strategies and pricing structures to prevent excessive pricing from leading to a decline in sales.
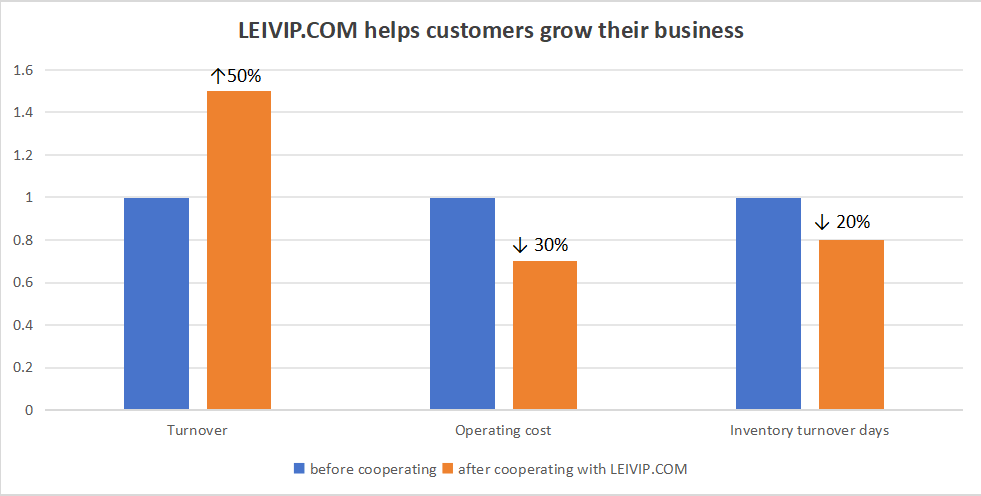
Brands that fail to adapt their Retail Prices to match market conditions risk losing their competitive edge and profitability. Developing strategies to stabilize Retail Prices is crucial for sustaining consumer trust and market share.
Supply Chain Pressures: Global Logistics Bottlenecks and Transportation Costs
Supply chain disruptions present another significant challenge. The global logistics system has yet to fully recover to its pre-pandemic state, resulting in prolonged shipping times and increased transportation costs. In 2023, due to congestion at major global ports and labor shortages, transportation costs rose by 15% to 20%, with no immediate signs of decline.
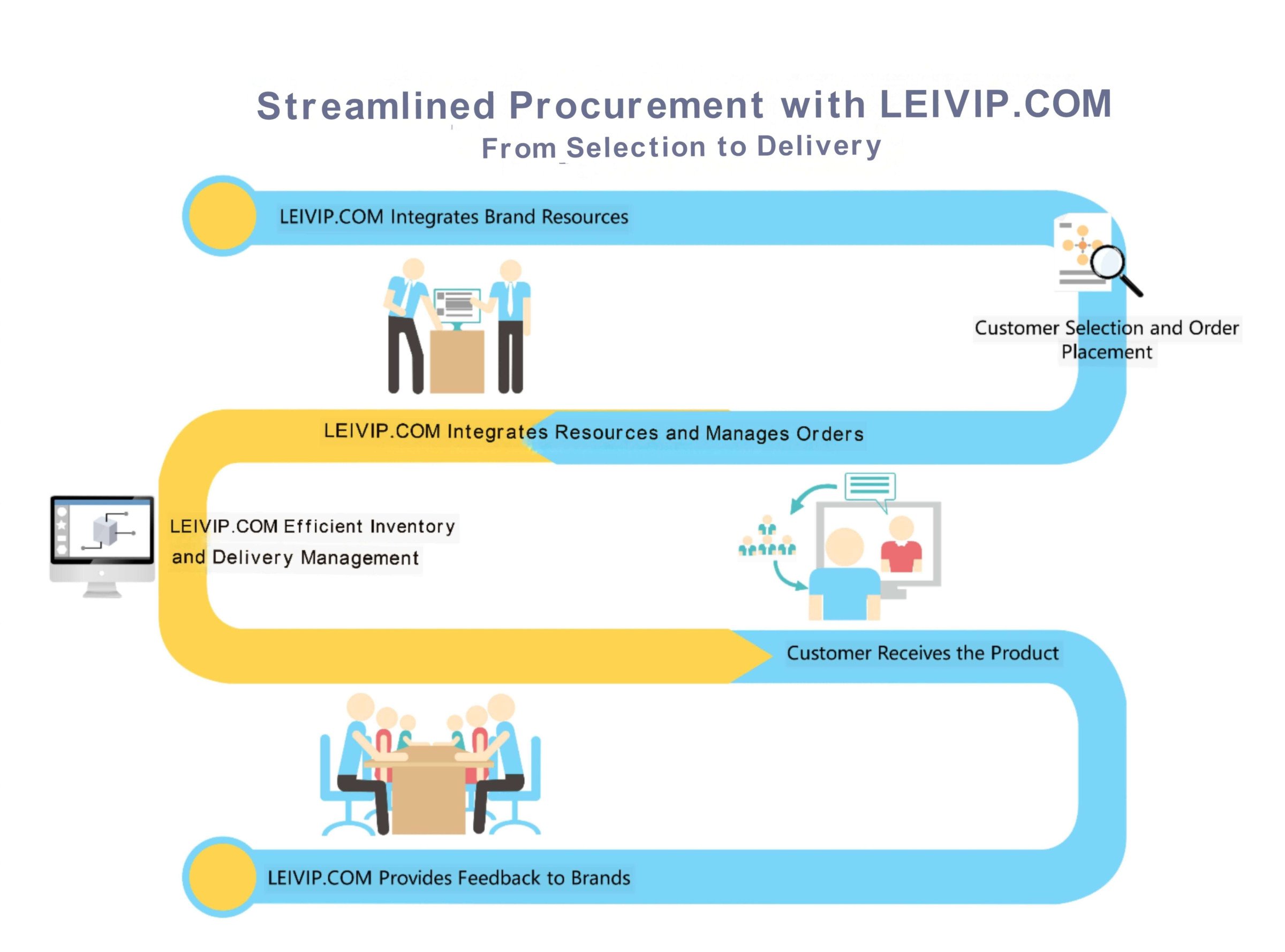
For fashion brands, increased transportation costs for production materials have led to extended overall production cycles. This not only raises production costs but also affects the market's responsiveness to new products. For instance, in high-end fashion brands with longer production cycles, logistics delays have postponed the launch of new products, impacting sales plans and profitability. Brands urgently need to seek more flexible and efficient supply chain management methods to address the challenges posed by logistics bottlenecks and ensure stable Retail Prices.
Efficient logistics planning can help mitigate these cost increases, ensuring Retail Prices remain competitive while preserving profitability. Leveraging innovative supply chain solutions is essential to maintain steady Retail Prices even during disruptions.
Declining Consumer Purchasing Power: Weakening Market Demand
The impact of inflation extends to consumer purchasing power. As multiple global economies enter low-growth phases, consumer spending willingness has significantly decreased. According to McKinsey's "Global Consumer Trends Report," in 2023, consumer spending growth slowed in several markets, with notable declines in sales of high-end luxury goods and fast fashion items.
In this context, retailers and brands face two choices: either pass the increased costs onto consumers through higher Retail Prices or compress profits to maintain sales. However, raising Retail Prices may lead to a decline in sales, as consumers become more price-sensitive. This situation implies that brands could face dual pressures on profits and market share. To address this challenge, brands must develop targeted pricing strategies that balance rising costs with affordable Retail Prices for consumers.